⚕️ MEDICAL DISCLAIMER
Important: This article is for informational purposes only and is based on research from peer-reviewed studies, dermatological publications, and expert medical sources. The content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. The author is not a medical professional but a content researcher who compiles expert recommendations. Always consult with a board-certified dermatologist or healthcare provider before starting any new hair loss treatment, especially if you have underlying health conditions, allergies, or are pregnant/nursing. Individual results may vary. This article contains affiliate links; we may earn a commission if you purchase through our links at no additional cost to you.
Introduction
Hair loss affects approximately 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States alone, according to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD). Whether you’re experiencing thinning hair, a receding hairline, or excessive shedding, finding effective solutions can feel overwhelming.
While pharmaceutical treatments like minoxidil and finasteride are clinically proven options, many people prefer to start with natural remedies supported by scientific research. This comprehensive guide examines 10 natural approaches to hair loss that have backing from dermatological studies, clinical trials, or expert recommendations.
It’s important to understand that natural doesn’t always mean “as effective as prescription treatments,” but research shows these remedies can support scalp health, strengthen existing hair, and in some cases, promote new growth when used consistently over several months.
What You’ll Learn in This Article:
- The scientific evidence behind 10 natural hair loss remedies
- How each remedy works according to dermatological research
- Realistic expectations and usage guidelines
- Which remedies have the strongest research support
- Safety considerations and potential side effects
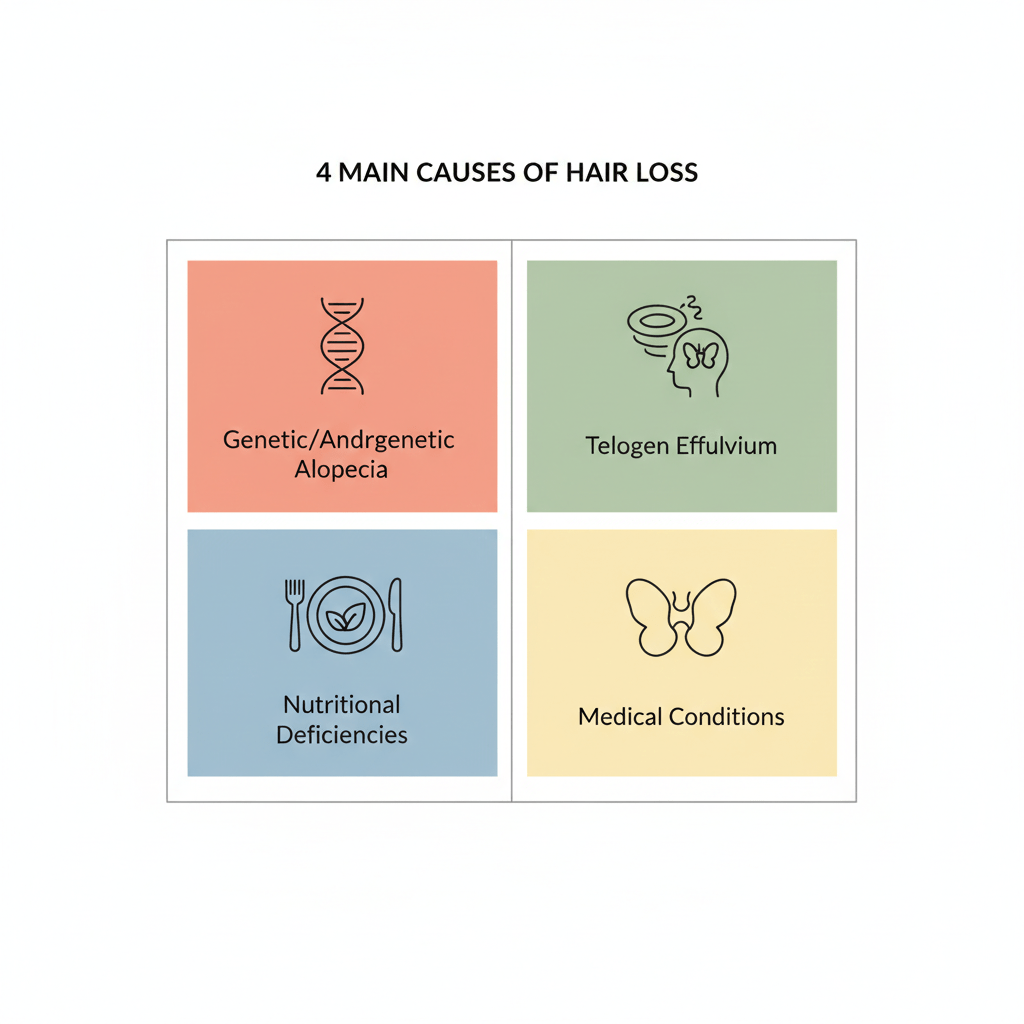
Understanding Hair Loss: What Causes It?
Before exploring remedies, it’s helpful to understand what causes hair loss. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, common causes include:
Androgenetic Alopecia (Pattern Hair Loss)
The most common type, affecting both men and women. Research published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology indicates this is caused by genetic sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone.
Telogen Effluvium (Stress-Related Shedding)
A temporary condition where stress, illness, or hormonal changes push hair follicles into a resting phase. The International Journal of Trichology notes this typically resolves within 6-9 months.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Deficiencies in iron, biotin, vitamin D, and protein can contribute to hair loss, according to research in Dermatology Practical & Conceptual.
Medical Conditions
Thyroid disorders, autoimmune conditions (alopecia areata), and hormonal imbalances can all cause hair loss.
Important: If you’re experiencing sudden or severe hair loss, consult a dermatologist to rule out underlying medical conditions before trying home remedies.
10 Natural Remedies for Hair Loss (Research-Backed)
1. Castor Oil
Evidence Level: ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate – mostly anecdotal with some supporting research)
What Research Shows:
Castor oil contains approximately 90% ricinoleic acid, an omega-9 fatty acid with anti-inflammatory properties. A 2015 study in the International Journal of Trichology found that ricinoleic acid can improve scalp circulation and reduce inflammation, both factors that support healthy hair growth.
However, direct clinical evidence specifically for hair growth is limited. The American Academy of Dermatology notes that while castor oil is safe for topical use and may improve scalp health, claims of dramatic hair regrowth lack robust scientific validation.
How to Use (According to Dermatologists):
- Warm 2-3 tablespoons of cold-pressed castor oil
- Massage gently into scalp for 5-10 minutes to improve circulation
- Leave on for 30 minutes to overnight
- Shampoo thoroughly (castor oil is thick and requires thorough washing)
- Use 2-3 times per week for at least 3 months to see potential results
Safety Note: Patch test first, as some people may have allergic reactions. Avoid if you have seborrheic dermatitis without consulting a dermatologist first.
2. Biotin (Vitamin B7)
Evidence Level: ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Strong for deficiency-related hair loss)

What Research Shows:
Biotin is a B-vitamin essential for keratin production, the protein that makes up hair. Research published in Skin Appendage Disorders found that biotin supplementation significantly improved hair growth in patients with underlying biotin deficiency.
A 2017 review in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology examined multiple studies and concluded that biotin supplements can improve hair thickness and reduce shedding in people with documented biotin deficiency. However, the review noted that benefits for people without deficiency are less clear.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) states that true biotin deficiency is rare, but marginal deficiencies may contribute to thinning hair.
How to Use (According to NIH Guidelines):
- Recommended daily intake: 30 mcg for adults
- Therapeutic doses in studies: 2,000-5,000 mcg daily
- Best absorbed from food sources: eggs, almonds, sweet potatoes, spinach
- Supplements should be taken for at least 3-6 months to assess effectiveness
Foods High in Biotin:
- Egg yolks (10 mcg per egg)
- Almonds (1.5 mcg per ounce)
- Sweet potatoes (2.4 mcg per 1/2 cup)
- Salmon (5 mcg per 3 oz)
Safety Note: Generally safe, but high doses can interfere with certain lab tests. Consult your doctor if taking medications or planning lab work.
3. Saw Palmetto
Evidence Level: ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Strong for androgenetic alopecia)
What Research Shows:
Saw palmetto extract may work similarly to finasteride by inhibiting 5-alpha-reductase, the enzyme that converts testosterone to DHT (dihydrotestosterone), the hormone responsible for pattern hair loss.
A 2020 meta-analysis published in Dermatologic Therapy reviewed multiple clinical trials and found that saw palmetto improved hair density and count in men with androgenetic alopecia. One study showed a 60% improvement rate compared to 11% in the placebo group.
Research in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine found that 320mg daily of saw palmetto extract improved hair growth in 38% of participants after 24 weeks.
How to Use (Based on Clinical Studies):
- Standard dose: 320mg daily (standardized extract)
- Topical formulations: Some studies used saw palmetto in topical solutions
- Duration: Minimum 6 months to see results (similar timeline to finasteride)
- Works best for pattern hair loss, not other types
Safety Note: Can interact with blood thinners and hormone medications. May cause mild digestive upset. Not recommended during pregnancy. Consult a healthcare provider before use.
4. Rosemary Essential Oil
Evidence Level: ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Strong – comparable to minoxidil in studies)
What Research Shows:
This is one of the most well-researched natural remedies. A 2015 clinical trial published in SKINmed compared rosemary oil to 2% minoxidil (Rogaine) in patients with androgenetic alopecia. After 6 months, both groups showed significant hair growth with no statistical difference between them.
Researchers believe rosemary oil works by improving circulation to the scalp and potentially acting as a mild DHT inhibitor. A study in Phytotherapy Research found rosemary extract inhibited 5-alpha-reductase activity.
The American Academy of Dermatology acknowledges rosemary oil as a promising natural alternative worth considering.
How to Use (According to Clinical Studies):
- Dilute essential oil: Never apply pure essential oil directly (can cause irritation)
- Ratio: 3-5 drops of rosemary essential oil per tablespoon of carrier oil (jojoba, coconut, or olive oil)
- Massage into scalp for 5 minutes, leave on for at least 30 minutes (or overnight)
- Use twice weekly minimum; daily use showed best results in studies
- Must be used for at least 6 months consistently
Safety Note: Can cause allergic reactions in some people. Patch test first. Avoid during pregnancy unless approved by doctor. Never ingest essential oils.
5. Pumpkin Seed Oil
Evidence Level: ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Strong – multiple clinical trials)
What Research Shows:
A 2014 randomized, placebo-controlled study published in Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that 400mg daily of pumpkin seed oil increased hair count by 40% after 24 weeks in men with androgenetic alopecia.
Researchers believe pumpkin seed oil works by inhibiting 5-alpha-reductase (similar to saw palmetto and finasteride) due to its phytosterol content. It also contains zinc, vitamin E, and omega fatty acids that support hair health.
A follow-up study in the Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology confirmed these findings with similar results.
How to Use (Based on Research Protocols):
- Oral supplementation: 400mg daily (standardized pumpkin seed oil capsules)
- Topical application: Can also be massaged into scalp, though oral supplementation showed stronger results in studies
- Timeline: 6 months minimum for visible results
- Works best for androgenetic alopecia
Safety Note: Generally safe. May cause mild digestive upset. Can interact with blood pressure medications. Consult doctor if you have prostate issues or are on medications.

6. Aloe Vera
Evidence Level: ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate – supports scalp health)
What Research Shows:
While direct evidence for hair regrowth is limited, research published in the Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research found that aloe vera contains enzymes that can remove dead skin cells from the scalp, potentially unclogging hair follicles.
A study in Pharmacognosy Magazine showed aloe vera’s anti-inflammatory properties can soothe scalp conditions like seborrheic dermatitis, which can contribute to hair loss. The NIH notes that aloe vera is rich in vitamins A, C, E, and B12, all of which support healthy hair.
The American Academy of Dermatology recommends aloe vera as a supportive treatment for scalp health rather than a primary hair growth treatment.
How to Use:
- Use pure aloe vera gel (99% aloe, minimal additives)
- Apply directly to scalp 2-3 times per week
- Leave on for 30-60 minutes before washing
- Can be mixed with essential oils like rosemary for enhanced benefits
- Best for soothing inflamed scalp and maintaining healthy follicle environment
Safety Note: Generally very safe. Rare allergic reactions possible. Patch test if you have sensitive skin.
7. Onion Juice
Evidence Level: ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Strong – surprising research support)
What Research Shows:
This might sound unusual, but onion juice has solid research backing. A 2002 study in the Journal of Dermatology found that applying onion juice to the scalp resulted in hair regrowth in 74% of participants with alopecia areata after 6 weeks (compared to 13% in the control group).
A 2014 follow-up study in the Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics found similar results, attributing benefits to onion’s high sulfur content, which may boost collagen production and improve blood circulation to hair follicles.
How to Use (Based on Study Protocols):
- Extract juice from fresh onions using a blender or grater
- Apply directly to scalp and leave on for 15-30 minutes
- Wash thoroughly with mild shampoo (smell can be strong)
- Use twice daily for at least 2 months
- Results in studies appeared within 4-6 weeks
Practical Tips:
- The smell is the main downside (very strong)
- Mixing with lemon juice or essential oils can help mask odor
- Some people refrigerate the juice to reduce smell
- Fresh juice works best; make small batches
Safety Note: Can cause skin irritation in some people. Patch test first. If you have sensitive skin, dilute with water. Avoid getting in eyes.
8. Coconut Oil
Evidence Level: ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate – preventive benefits documented)
What Research Shows:
While coconut oil hasn’t been proven to stimulate new hair growth, research published in the Journal of Cosmetic Science found it’s one of the few oils that can actually penetrate the hair shaft to prevent protein loss and damage.
A study in International Journal of Trichology showed that coconut oil reduces hair breakage and helps maintain hair integrity better than mineral oil and sunflower oil. The lauric acid in coconut oil has antimicrobial properties that can support scalp health.
According to dermatology research, coconut oil is best viewed as a protective and conditioning treatment rather than a growth stimulator.
How to Use:
- Use virgin, unrefined coconut oil for maximum benefits
- Warm slightly (it’s solid at room temperature)
- Apply to hair and scalp, focusing on ends
- Leave on for 30 minutes to overnight
- Shampoo thoroughly (may require two washes)
- Use 1-2 times per week
Best For:
- Preventing breakage and damage
- Conditioning dry, damaged hair
- Protecting hair during chemical treatments
- Supporting overall hair health
Safety Note: Can make fine hair appear greasy or limp. May clog pores in some people if left on scalp too long. Generally safe for most people.
9. Green Tea (Topical Application)
Evidence Level: ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate – promising early research)
What Research Shows:
Green tea contains epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a polyphenol that research suggests may promote hair growth. A study in Nutrients found that EGCG stimulated hair follicles and prevented hair loss by blocking DHT production.
Research published in the British Journal of Dermatology showed topical EGCG application improved hair density in early studies. A study in Phytomedicine found green tea extract extended the anagen (growth) phase of hair follicles.
While promising, most studies have been conducted on mice or in vitro, with limited human clinical trials. More research is needed to confirm effectiveness in humans.
How to Use:
- Brew strong green tea (2-3 tea bags in 1 cup hot water)
- Let cool to room temperature
- Apply to scalp and massage gently
- Leave on for 30-60 minutes
- Rinse with cool water
- Use 2-3 times per week
Alternative: Take green tea extract supplements (studies used 300-400mg EGCG daily)
Safety Note: Generally safe topically. Oral supplements may interact with blood thinners and certain medications. Contains caffeine, which may affect sleep if taken as a supplement. Consult doctor if on medications.
10. Peppermint Oil
Evidence Level: ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Strong – outperformed minoxidil in animal studies)

What Research Shows:
A 2014 study in Toxicological Research compared peppermint oil to minoxidil and saline in mice. Surprisingly, peppermint oil showed significantly better results than 3% minoxidil, increasing hair follicle number and depth.
Researchers attribute benefits to menthol’s ability to increase blood flow to the scalp by dilating blood vessels. A study in Experimental Dermatology confirmed peppermint oil’s vasodilatory effects.
While human clinical trials are limited, the American Academy of Dermatology notes peppermint oil as a promising natural option based on preliminary research.
How to Use (Safely):
- NEVER apply undiluted – essential oils are highly concentrated
- Dilution: 2-3 drops peppermint oil per tablespoon carrier oil (jojoba, coconut)
- Massage into scalp, leave on 20-30 minutes before washing
- Tingling sensation is normal; burning or severe irritation is not
- Use 2-3 times per week
- Minimum 4-6 weeks to see potential results
Why Dilution Matters: Pure peppermint oil can cause severe scalp irritation, chemical burns, or allergic reactions. Always dilute properly.
Safety Note: Patch test mandatory. Can cause allergic reactions. Avoid during pregnancy. Keep away from eyes. Not for use on children or pets.
Comparison Chart: Which Remedies Have the Strongest Evidence?
| Remedy | Evidence Strength | Best For | Time to Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rosemary Oil | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Pattern hair loss | 6 months |
| Pumpkin Seed Oil | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Pattern hair loss (men) | 6 months |
| Saw Palmetto | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | DHT-related loss | 6 months |
| Onion Juice | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Alopecia areata | 6-8 weeks |
| Peppermint Oil | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | General growth stimulation | 4-6 weeks |
| Biotin | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Deficiency-related loss | 3-6 months |
| Castor Oil | ⭐⭐⭐ | Scalp health | 3 months |
| Aloe Vera | ⭐⭐⭐ | Scalp conditions | 2-3 months |
| Coconut Oil | ⭐⭐⭐ | Preventing breakage | Immediate |
| Green Tea | ⭐⭐⭐ | General support | 3-4 months |
Can You Combine Multiple Remedies?
Yes! In fact, combining remedies may provide better results. Research suggests a multi-pronged approach addressing different factors (DHT reduction, circulation, nutrition, scalp health) may be more effective than any single remedy.
Safe Combination Example:
- Internal: Biotin supplement (2,000 mcg daily) + Pumpkin seed oil (400mg daily)
- Topical: Rosemary oil scalp massage (3x weekly) + Coconut oil conditioning (weekly)
- Dietary: Green tea daily + biotin-rich foods
Important: Always patch test new topical treatments and introduce one new supplement at a time to monitor for reactions.

When to See a Dermatologist
While natural remedies can be effective, certain situations require professional medical evaluation:
- Sudden or severe hair loss (more than 100-150 hairs daily)
- Patchy bald spots (may indicate alopecia areata)
- Hair loss accompanied by scalp pain, itching, or redness
- No improvement after 6 months of consistent natural treatment
- Hair loss in children or teenagers
- Suspicion of underlying medical condition (thyroid issues, hormonal imbalance)
A dermatologist can:
- Diagnose the specific type of hair loss
- Rule out medical causes
- Prescribe FDA-approved treatments (minoxidil, finasteride)
- Recommend procedures (PRP therapy, laser treatments)
- Create a comprehensive treatment plan

Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to see results from natural remedies?
Most natural remedies require 3-6 months of consistent use before visible results. Hair growth is slow – the average rate is only 0.5 inches per month. According to dermatology research, the hair growth cycle means you won’t see new growth for at least 2-3 months even with effective treatment. Be patient and consistent.
Can natural remedies work as well as prescription treatments?
Some can come close. Studies show rosemary oil performed similarly to 2% minoxidil, and saw palmetto showed results comparable to finasteride in some studies. However, the American Academy of Dermatology notes that prescription treatments (minoxidil and finasteride) have the most robust clinical evidence. Natural remedies are best viewed as alternatives for those who prefer to avoid medications or as complementary treatments.
Are natural remedies safe for everyone?
Not necessarily. “Natural” doesn’t mean “risk-free.” Essential oils can cause allergic reactions, saw palmetto can interact with medications, and biotin can interfere with lab tests. Always patch test topical treatments, consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements, and discontinue use if you experience adverse reactions.
Can I use these remedies if I’m pregnant or breastfeeding?
Most essential oils and herbal supplements are not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding without medical approval. Biotin and food-based remedies are generally safe, but always consult your OB-GYN or healthcare provider first.
Will my hair grow back if I stop using these remedies?
This depends on the cause of your hair loss. For androgenetic alopecia (pattern hair loss), hair loss will likely resume if treatment is stopped, similar to prescription treatments. For temporary hair loss (telogen effluvium, nutritional deficiency), hair may continue growing normally after the underlying cause is addressed.
How much hair loss is normal?
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, losing 50-100 hairs per day is normal. If you’re consistently losing more than this, experiencing visible thinning, or noticing excess hair in your brush or shower drain, consult a dermatologist.
Can diet affect hair loss?
Yes. Research in Dermatology Practical & Conceptual shows that deficiencies in iron, vitamin D, biotin, protein, and zinc can all contribute to hair loss. A balanced diet rich in these nutrients supports healthy hair growth. However, diet alone may not resolve genetic pattern hair loss.
Do these remedies work for all types of hair loss?
No. Different types of hair loss respond to different treatments:
- Pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia): Best respond to DHT blockers like saw palmetto, pumpkin seed oil, rosemary oil
- Alopecia areata: Onion juice showed specific benefits in studies
- Telogen effluvium: Often resolves on its own; supportive scalp care helpful
- Nutritional deficiency: Biotin and nutritional support
- Scarring alopecia: Requires medical treatment; natural remedies ineffective
The Bottom Line
Natural remedies for hair loss can be effective, especially when:
- Used consistently for 6+ months
- Appropriate for your specific type of hair loss
- Combined with a healthy diet and stress management
- Expectations are realistic
The most promising natural remedies based on research:
- Rosemary oil – Comparable to minoxidil in clinical trials
- Pumpkin seed oil – 40% increase in hair count in studies
- Saw palmetto – DHT blocker with clinical evidence
- Onion juice – Surprisingly strong results for alopecia areata
- Biotin – Effective for deficiency-related hair loss
Remember: Hair growth takes time. The hair growth cycle means even effective treatments won’t show visible results for 2-3 months minimum. Consistency is key.
If natural remedies don’t provide sufficient results after 6 months, or if you’re experiencing severe or sudden hair loss, consult a board-certified dermatologist to explore all treatment options, including FDA-approved medications and procedures.
About the Author
Karine is a health content researcher and writer who specializes in compiling expert advice from medical journals, dermatological publications, and authoritative health sources. While not a medical professional herself, she ensures all health-related content cites peer-reviewed research and expert recommendations. Karine creates evidence-based guides to help readers make informed decisions about their health and wellness.
Sources Consulted
This article was researched using the following authoritative sources:
- American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) – Hair Loss: Diagnosis and Treatment https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/hair-loss
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Office of Dietary Supplements: Biotin Fact Sheet https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Biotin-HealthProfessional/
- Journal of Dermatology – “Onion juice (Allium cepa L.), a new topical treatment for alopecia areata” (2002) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12126069/
- SKINmed – “Rosemary oil vs minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: a randomized comparative trial” (2015) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25842469/
- Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine – “Effect of Pumpkin Seed Oil on Hair Growth in Men with Androgenetic Alopecia” (2014) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24864154/
- International Journal of Trichology – Research on castor oil and hair health (2015) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26180450/
- Dermatologic Therapy – “Saw palmetto for hair loss: a systematic review” (2020) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32416620/
- Journal of Cosmetic Science – “Effect of mineral oil, sunflower oil, and coconut oil on prevention of hair damage” (2003) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12715094/
- Toxicological Research – “Peppermint Oil Promotes Hair Growth without Toxic Signs” (2014) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25343008/
- Dermatology Practical & Conceptual – “Diet and hair loss: effects of nutrient deficiency and supplement use” (2017) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5582478/
- British Journal of Dermatology – EGCG and hair follicle research https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30168143/
- Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine – Saw palmetto clinical trials https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22420620/
- Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology – “A Review of the Use of Biotin for Hair Loss” (2017) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28492390/
- Journal of Investigative Dermatology – DHT and pattern hair loss research https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11903391/
- Nutrients – “Green tea polyphenols and hair follicle health” (2018) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30096883/
Medical Review Note: While this article cites peer-reviewed research and expert sources, it has not been individually reviewed by a medical professional. Always consult a board-certified dermatologist for personalized medical advice.
Last Updated: 13 February 2026
Next Review Date: August 13, 2026
Related Articles on KnowsMyStyle.com
- How to Sleep Better: A Comprehensive Guide
- 7 Low-Investment Side Hustles You Can Start This Weekend
- How to Teach Kids to Be Grateful
Affiliate Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you purchase products through our links, we may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you. This helps support our research and content creation. We only recommend products mentioned in scientific studies or endorsed by reputable health organizations.
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "FAQPage",
"mainEntity": [
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "How long does it take to see results from natural remedies?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Most natural remedies require 3-6 months of consistent use before visible results. Hair growth is slow - the average rate is only 0.5 inches per month. The hair growth cycle means you won't see new growth for at least 2-3 months even with effective treatment."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Can natural remedies work as well as prescription treatments?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Some can come close. Studies show rosemary oil performed similarly to 2% minoxidil, and saw palmetto showed results comparable to finasteride in some studies. However, prescription treatments have the most robust clinical evidence."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Are natural remedies safe for everyone?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Not necessarily. Natural doesn't mean risk-free. Essential oils can cause allergic reactions, saw palmetto can interact with medications, and biotin can interfere with lab tests. Always patch test topical treatments and consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements."
}
}
]
}
</script>